|
Dry Support Bridge (DSB)

Any questions, comments, or problems, please email
me.

XM1975 Walk
Around by Don Busack
XM1975 Driving
by Don Busack
XM1975
DSB Unfolding by Don Busack
XM1975 DSB
Setting Up by Don Busack
DSB Information
The M18 DSB system brings a revolutionary change to the
Multirole Bridge Companies (MRBC). The Dry Support Bridge (DSB) relies on
a mechanical system to significantly reduce soldier effort and improve
operational capability to the force. The DSB replaces the medium girder
bridge (MGB), while doubling the gap-crossing capability of each MRBC. It is
intended to fill all 40-meter-or-less, dry-gap bridging roles from the brigade
rear to the communication zone ports in a variety of tactical situations.
Each MRBC is authorized four DSB systems, each consisting of
an M1975 launch vehicle and a modular bridge that can span gaps up to 40 meters.
A crew of eight soldiers can transport the entire system and deploy a 40-meter
bridge in 90 minutes or less. Bridge loads are modular and palletized onto
seven flatracks that are transported via organic Common Bridge Transporters (CBT)
and Palletized Load System (PLS) trailers. Soldiers can also construct two
shorter bridges, up to 22 and 28 meters long respectively, from each DSB system.
The M18 DSB system is composed of two subsystems, the M1975
launcher vehicle and the M19 DSB. The M1975 uses a hydraulically operated
launch system integrated onto a standard PLS chassis and a set of launch beams
that is carried as a separate palletized load. A launch beam is
cantilevered over the gap that supports the bridge as it is built and projected
across the gap. The labor required to emplace and remove the bridge is
significantly reduced by the use of an integrated, materiel-handling crane, as
well as by the ability of CBTs to maneuver the palletized bridge loads around
the construction site easily.
The M19 DSB is a modular, all-aluminum bridge. Although
some of the components seem similar in design to the MGB, the number of
components has been drastically reduced and the bridge is a new design. A
40-meter bridge consists of 2 ramp modules, 5 parallel modules, 2 end beams, 20
approach ramps, and 24 bridge pins. Each module has curbs and drivers’
aids integrated into it, and modules fold up onto themselves for transportation.
The bridge has a 4.3-meter roadway and supports Military Load Class (MLC) 80T
(tracked)/110W (wheeled). The bridge is also fielded with a new anchorage system
for longer-term use. To further reduce labor requirements, the anchorage
system features an onboard pneumatic hammer, which is powered via standard
connections to the launcher vehicle or organic CBTs.
The DSB program transitioned into full-rate production in May
2003 and attained full materiel release in June 2003. The Program Manager
for Bridging fielded four DSB systems to the 74th Multirole Bridge Company in
February 2003 just before its deployment to Southwest Asia, and the system
successfully supported operations there.
--- This data is from the April-June 2004 issue of Engineer,
by Lieutenant Colonel Andrew DiMarco. Content modified by Don Busack.
Dry Support Bridge Specifics
|
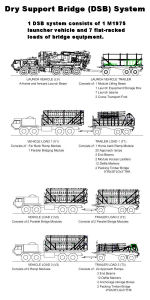
1 DSB System consists of:
-
1 Launch
vehicle + launch beams on LVT
-
Bridge
Load V1 - 2 parallel modules + T1 - Approach ramps/ramp module
-
Bridge
Load V2 - 2 parallel modules + T2 - 1 Parallel Module
-
Bridge
Load V3 - 2 ramp modules + T3 - Approach ramps
-
Crew of 8
soldiers
All trailer and M1977 loads are palletized loads, the
launch vehicle (M1975) is mounted on a PLS chassis, but is not removable.
The unit consists of:
|
Click for larger image |
| 